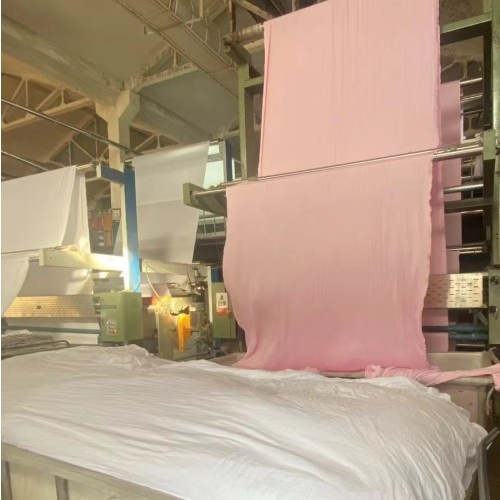
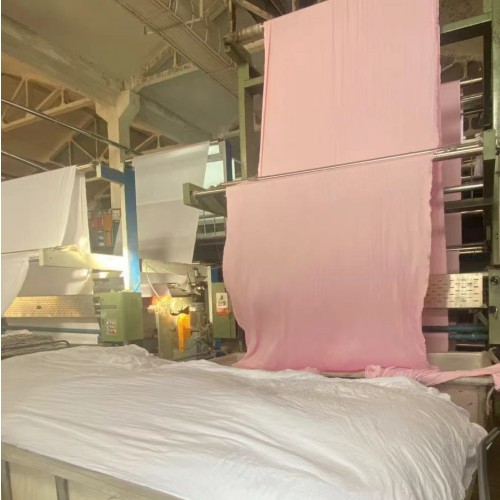
For dyed fabrics, gray fabrics (woven fabrics, knitted fabrics, etc.) are produced through professional dyeing equipment: packing, sewing, singeing, desizing and oxygen bleaching, mercerizing, shaping, dyeing, finishing, pre-shrinking and shaping. The finished cloth is dyed cloth.
Dye fastness is the most important indicator of dyed fabrics.The ability of printed and dyed textiles to withstand external influences and maintain their original color is also called color fastness.After dyeing and printing, textiles sometimes have to go through other processes, such as milling of wool fabrics, heat setting of synthetic fiber fabrics, etc.; during the wearing process, they are exposed to the atmosphere, sweat stains, and are subjected to external factors such as washing, friction, and ironing. effect.These can cause varying degrees of fading and discoloration of printed and dyed textiles.The processes that affect the color fastness of printed and dyed textiles are mainly milling, carbonization, chlorine bleaching, sublimation, etc.The color fastness of dyes or pigments on textiles is related to their chemical structure, concentration and state on the fiber, and the properties of the fiber.Various dye fastness test methods are developed to simulate various wearing or process conditions.










 Non-woven fabric
Non-woven fabric Textile accessories
Textile accessories